Categories of Knowledge for Bioinformatics Education
U = Undergrad. level G = Grad. level
C = CS S = Stats/Math B = Bio/Chem/Phys
I = Intro. Bioinformatics Topic (i.e., in a class like CBB752) A = Advanced Bioinformatics Topic (i.e., maybe beyond CBB752)
Combining Abbreviations - viz: UC, GC, US, GS, GI, GA, GB, UB
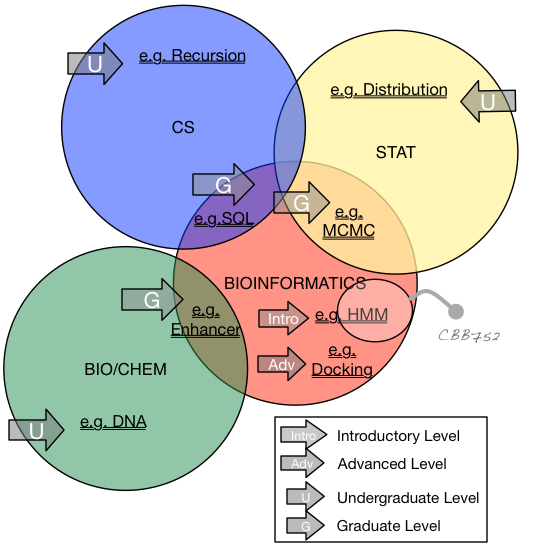
Prerequisites for Bioinformatics: Stats & CS
These go beyond Basic Math (calculus), Biology, Chemistry & Physics taught in pre-medical education and in undergraduate majors such as Yale MB&B
Programming Topics [UC]
-
Interpretative lang. & compiled lang.
-
Recursion
-
Data structures - lists, arrays, hashes, stacks
-
Computational complexity - related to operations as sorting
-
Basics of computer architecture (caches, disks, bottlenecks)
-
Practical Programming: modularization (OOP), version control, debugging, APIs & libraries, software carpentry, reproducible research/coding
-
Basics of web programming - stateless access, web protocols
-
Databases
-
Basics of SQL, with concept of indices & joining, schema
-
non-relational architectures - NoSQL
-
-
Regular expression & string processing
-
Numeric computing issues: FP arith & random numbers
-
Encryption & compression
Programming Topics [GC]
-
VMs & cloud computing
-
Optimization & integration of functions [US]
-
Relational Database Concepts and how they interface with Biological Information
-
DB interoperation
-
Privacy and security issues
-
Ontologies
-
Distributed and high-performance computing (parallel computing) [XH: I think this part is pretty important especially when dealing with large data and it should be included as GC since some of the techniques (like random number generation, MCMC, and running with GPU) is quite complicate in the parallel mode.]
Statistical Topics [US]
-
Knowledge of distributions, hypothesis testing & inference (includes mult. testing, T-test)
-
Permutation Testing (bootstrapping, cross-validation)
-
Regression
-
Power analysis (Type 1 & 2 errors)
-
Non-parametric vs. Parametric methods
-
Bayes Rule
Statistical Topics [GS]
-
Regularization
-
Unsupervised Methods (PCA, clustering)
-
Supervised Methods (SVM, Kernels)
-
Bayesian Analysis
-
Graphical Models
-
Causal inference
-
Missing data, imputation & EM algorithm
-
Hierarchical Modelling
-
Information theory - mut. information, complexity & entropy
-
Hidden Markov Models, Viterbi, Forward and Backward Algorithms, MCMC
-
Feature Selection
Prominent Stat/CS Topics NOT included
-
Interrupts
-
Machine language
-
Compiler design
-
Computer Graphics
-
Crypto
Specific Bioinformatics Topics
Classical Sequence Analysis
-
String Matching
-
Pairwise Alignment via Dynamic Programming [GI]
-
Local vs. Global Alignment & Suboptimal Alignment [GI]
-
Hashing & Indexing to increase speed (BLAST, FASTA) [GI]
- Suffix arrays & BWT
-
Substitution scoring matrices (e.g., for amino acids) [GI]
-
Scoring schemes & Matching statistics
- Score Distributions (e.g., EVD)
-
-
Multiple Alignment and Consensus Patterns
-
Identifying genomic regions such as genes & promoters with various statistical methods (e.g., HMMs) [GI]
-
HMMs, Profiles, Position dependent subst. matrices [GI]
-
Motifs [GI]
-
Expectation Maximization & Gibbs Sampling [GI]
-
Finding Structural RNAs
-
-
Whole-Genome analysis
-
Genome Assembly [GA]
- De Bruijn graph
-
Characterizing Repeats in Genomic DNA [GA]
-
Identification Duplications in the Genome [GA]
-
Whole-Genome Comparisons & large scale genomic alignments [GA]
-
Synteny
-
Function Classification & Orthologs
-
-
Genome Annotation
-
Gene Prediction
-
Regulatory site and network prediction
-
miRNA prediction and targeting site prediction
-
Pseudogene prediction and functional prediction
-
-
Next-Gen Sequencing Data Processing
-
Variant Calling
-
Germline
-
Somatic
-
Structural variation & rearrangements
-
-
RNA-seq
-
Recognizing and correcting batch effects
-
Transcript assembly & splicing
-
Quantification [GI]
-
eQTLs & allelic transcription
-
Normalization
-
Expression Analysis
-
Time Courses clustering/longitudinal clustering (which is more common in human clinical visits data)
-
Measuring differences
-
-
-
DNA methylation & epigenetic gene regulation
-
ChIP-seq
-
Peak calling
-
-
Metagenomics (microbiome) [GA]
Statistical Genetics [GA]
-
Population Genetics & Allele Freq.
-
Genotype-Phenotype Associations
-
Case-control & GWAS
-
Correlation vs. causality
-
QTLs
-
-
Survival Analysis
-
Evolutionary Issues
-
Rates of mutation and change
-
Clustering & Trees [GI]
- Distance vs. maximum likelihood tree methods
-
Processing Other Big Data Sets
-
Flow Cytometry & CyTOF data analysis
-
Proteomics (Mass Spec)
-
Metabolomics [GA]
-
Literature Mining
-
Structural Genomics
-
Non-Image processing
Data Integration & Mining
-
Information integration and fusion
- Dealing with heterogeneous data
-
Ensemble Learning
-
Dimensionality Reduction (PCA etc.)
-
Assessing Predictions
-
Training and testing data
-
Cross validation
-
ROC curves
-
-
Network Analysis
-
Pathway analysis
-
Topology Analysis (Hubs & Bottlenecks)
-
Prediction of linkages
-
Global structure vs. local network motifs
-
-
Meta-analysis
- Fisher’s Method for combining p-values
Sequence to Structure
-
Secondary Structure Prediction
-
via Propensities
-
TM-helix finding
-
-
Tertiary Structure Prediction
-
Homology Modeling & Protein Threading (Fold Recognition)
-
Ab initio
-
-
Direct Function Prediction
- Active site identification
-
Structure Prediction: Protein vs. RNA
3D Structure Analysis
-
Molecular Geometry
-
Distances, Angles, Axes, Rotations
-
Calculating a helix axis in 3D via fitting a line
-
Molecular Graphics
-
-
Calculation of Volume and Surface
-
Hinge prediction
-
Packing Measurement
-
-
-
Structural Comparison & Alignment
-
Basic Protein Geometry and Least-Squares Fitting
-
Aligning sequences on the basis of 3D structure
-
Fold Library
-
-
Docking and Drug Design [GA]
-
EM image analysis
Simulation & Modelling
-
Molecular Mechanics
-
Basic interactions, potential energy functions
-
Geometry => Energy => Forces
-
Covalent
-
Bonds & Angles (as springs)
-
Dihedral
-
-
Noncovalent
-
Electrostatics
-
VDW Forces
-
-
-
Energy Minimization
- Steepest Descent & Conjugate Gradient
-
Molecular Dynamics & MC
-
-
Simplifications
-
Poisson-Boltzmann Equation
-
Lattice Models & Progressive Simplification
-
-
Signaling & Pathway Modeling
-
Population Dynamics w/ ODEs
-
Regulatory network modeling via Boolean networks, ODEs
-
Flux-balance calculations
-
-
Viral Dynamics